One of the most effective ways to protect your PC from unauthorized access and cyberattacks is through Two-Factor Authentication (2FA). This simple but powerful security measure can add an extra layer of protection to your online accounts and local data. In this article, we’ll explore how Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) works and how it can significantly boost your PC’s security.
What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security process that requires two forms of identification to verify a user’s identity. Unlike traditional methods where you only need a password, 2FA combines something you know (like a password) with something you have (like a smartphone or hardware token). This additional step makes it exponentially more difficult for cybercriminals to access your accounts or PC, even if they have stolen your password.
There are various methods of 2FA, including:
- SMS or email codes: A one-time code sent to your phone or email.
- Authenticator apps: Apps like Google Authenticator or Authy that generate time-sensitive codes.
- Biometric authentication: Fingerprints, face recognition, or retina scans.
- Hardware tokens: Physical devices that generate unique login codes.
By implementing 2FA, you are effectively reducing the risk of unauthorized access to your data, ensuring that your personal information is kept safe.
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Boost Your PC’s Security?
1. Stronger Protection Against Password Breaches
Passwords are often the first line of defense for protecting our devices and online accounts. However, many users rely on weak passwords that are easy to guess, reuse passwords across multiple sites, or fall victim to phishing scams. Even if you follow best practices for creating strong passwords, they can still be compromised through data breaches, keylogging, or brute-force attacks.
By enabling 2FA, you make it harder for attackers to gain access to your PC and online accounts, as the process requires not only your password but also a second authentication factor that only you possess (e.g., your phone or a fingerprint). Even if someone manages to steal your password, they would still need the second factor to complete the login process.
2. Protects Your Sensitive Data from Cyberattacks
A PC is often a treasure trove of sensitive information, including personal documents, banking information, work-related files, and login credentials. Cyberattacks like phishing, ransomware, and man-in-the-middle attacks are designed to exploit vulnerabilities in your system to access this data. Two-Factor Authentication acts as an extra defense layer against these attacks.
For instance, in a phishing attack, an attacker may trick you into entering your login credentials on a fake website. If you have 2FA enabled, even if your password is compromised, the attacker still won’t be able to log in without the second authentication factor, which is in your possession.
3. Safeguards Your Online Accounts Linked to Your PC
For many people, online accounts such as email, social media, cloud storage, and even bank accounts are directly linked to their PCs. Cybercriminals often target these accounts, as they are gateways to sensitive information. Once they gain access, they can steal data, cause financial damage, or cause harm to your reputation.
By enabling 2FA for these online accounts, you reduce the chances of unauthorized access. Even if a hacker manages to obtain your password through a data breach, the additional verification step required for 2FA prevents them from easily accessing your account, keeping your data safe.
4. Enhances Remote Access Security
With the rise of remote work and the increasing reliance on cloud services, many people access their PCs and files remotely via Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), or cloud platforms like Google Drive or Dropbox. Unfortunately, remote access increases the risk of unauthorized access if not properly secured.
Implementing 2FA for your remote services ensures that even if someone intercepts your login credentials while you’re working remotely, they won’t be able to gain access without the second factor. This is especially important when accessing sensitive business data or handling confidential documents remotely.
5. Adds an Extra Layer of Security for Administrators
If you’re managing a business or network, 2FA becomes even more critical. Administrative accounts have higher privileges, meaning that unauthorized access can lead to severe consequences such as data breaches or system manipulation. By enabling 2FA on administrative accounts, you add an extra layer of security that helps prevent unauthorized users from making significant changes to your system or network.
6. Increased Security for Mobile Devices Linked to Your PC
In today’s world, mobile phones and PCs are often linked for syncing files, managing emails, or accessing cloud services. Since mobile devices are more prone to theft, enabling 2FA for accounts and services accessed from your PC ensures that even if your phone is lost or stolen, your data is protected. The thief would still need the second authentication factor (like your fingerprint or a verification code sent to your phone) to access your accounts.
How to Set Up Two-Factor Authentication on Your PC
Setting up 2FA on your PC is straightforward and can be done in a few simple steps. Here’s a general guide on how to enable 2FA for your operating system and online accounts.
1. Enable Two-Factor Authentication on Windows 10/11
While Windows doesn’t offer 2FA natively for local accounts, you can enable it for Microsoft accounts linked to your PC.
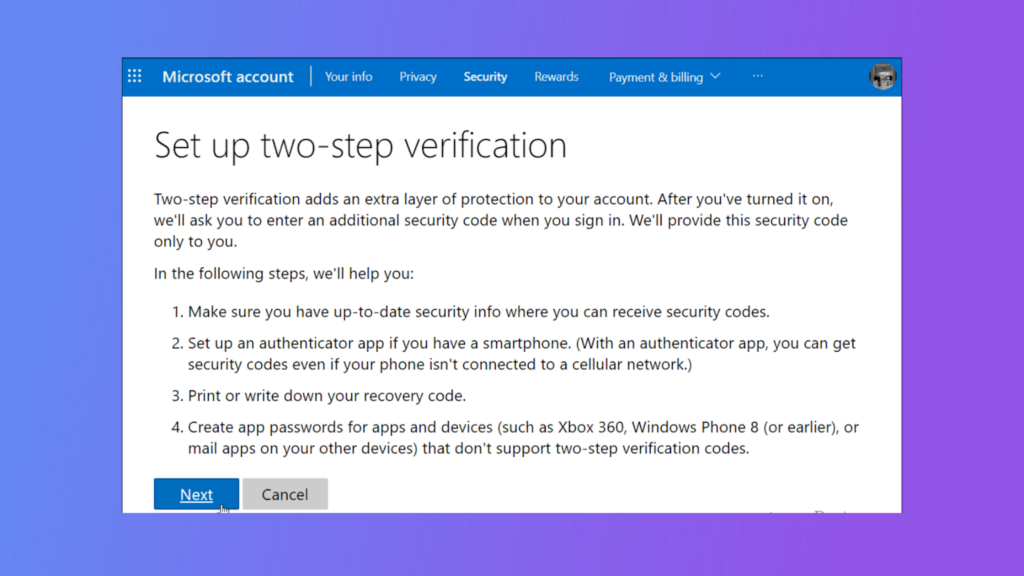
- Open Settings by pressing Windows + I.
- Click on Accounts > Your Info.
- Select Sign in with a Microsoft account instead (if not already signed in with one).
- Visit the Microsoft Account Security page (https://account.microsoft.com/security).
- Click Advanced Security Options.
- Under Two-Step Verification, click Turn on and follow the prompts to set up 2FA.
Once activated, you’ll need your password and a verification code (sent to your phone or email) to log in.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication for Online Accounts
For popular services like Google, Facebook, Dropbox, or Amazon, enabling 2FA is essential. Here’s a quick guide on enabling 2FA on Google:
- Go to Google Account Settings (https://myaccount.google.com/).
- Select Security from the menu.
- Under Signing in to Google, click 2-Step Verification and then Get Started.
- Follow the prompts to add your phone number and choose your second authentication method (e.g., Google Authenticator app or text message).
Repeat this process for other services you use, and ensure your accounts are fully protected.
Best Practices for Two-Factor Authentication
While 2FA offers robust protection, it’s important to follow best practices to get the most out of this security feature:
- Use Authenticator Apps Over SMS: Authenticator apps (like Google Authenticator or Authy) are more secure than SMS-based 2FA since they are not susceptible to SIM swapping attacks.
- Enable Backup Codes: Some services allow you to generate backup codes in case you lose access to your second factor. Store them securely.
- Update Recovery Options: Ensure that your email address and phone number are always up-to-date so you can recover your account if needed.
Conclusion
In an age where cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated, Two-Factor Authentication provides an extra layer of protection that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to your PC and online accounts. By implementing 2FA, you are making it harder for attackers to compromise your data, safeguard sensitive information, and enhance the security of your PC overall.
Whether you’re managing personal data or running a business, enabling 2FA is one of the most effective steps you can take to protect your information and prevent cyber threats from affecting your system.







